The Scope of the Compromise: Understanding 19 Billion Compromised Passwords
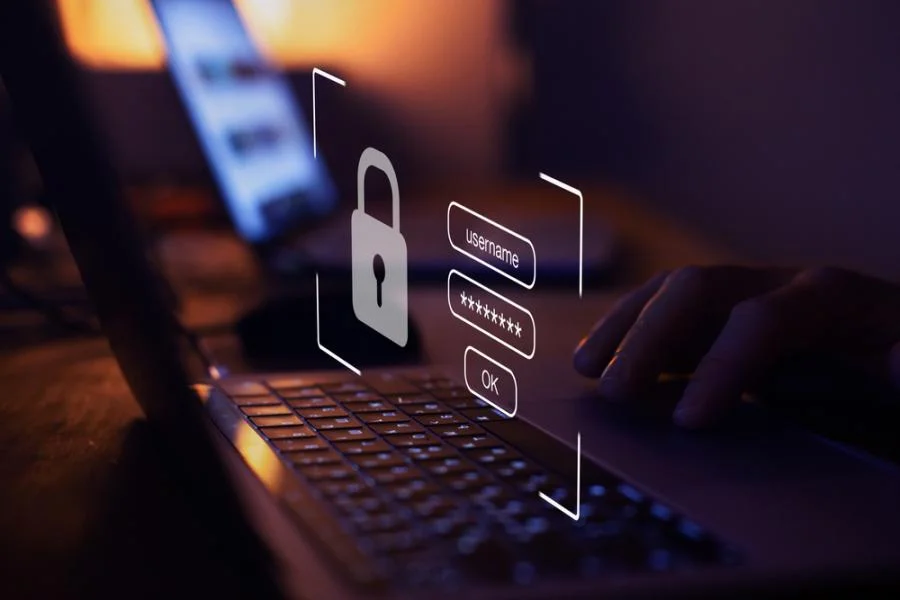
The staggering figure of 19 billion compromised passwords represents a significant threat to cybersecurity across the globe. This immense number stems from numerous data breaches that have occurred over the years, affecting countless organizations. High-profile incidents, such as the breaches of major tech companies and online platforms, have contributed to this alarming total. These incidents often result from inadequate security measures, phishing attacks, and other cyber vulnerabilities that are exploited by malicious actors.
Password databases, once stolen, are frequently made available on dark web forums, allowing cybercriminals to use these credentials for various nefarious purposes. For individuals, the implications can be dire. A compromised password can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive accounts, resulting in identity theft, financial losses, and other forms of cybercrime. Furthermore, the cascading effect of compromised accounts can lead to additional breaches, as individuals often use similar passwords across multiple platforms.
Organizations must be proactive in addressing these threats by implementing strong password policies, encouraging the use of multi-factor authentication, and educating employees about the dangers of phishing schemes. The sheer scale of 19 billion compromised passwords serves as a reminder that both individuals and organizations must prioritize their online security. As cyber threats evolve, staying informed and adapting security practices is essential in mitigating risks associated with compromised credentials.
How Compromised Passwords Are Used by Cybercriminals
The reality of cybercrime today is underscored by the staggering number of 19 billion compromised passwords circulating online. Cybercriminals exploit these passwords through various techniques that cause irreparable damage to individuals and organizations alike. One prevalent method is credential stuffing, where attackers use automated tools to try stolen usernames and passwords across multiple accounts. Since many individuals tend to recycle passwords across different sites, a single breach can grant attackers access to various unrelated platforms, ranging from email to banking services.
Phishing represents another threatening avenue in which compromised passwords come into play. Cybercriminals often craft deceptive emails or websites that mimic legitimate services, tricking unsuspecting users into entering their credentials. Once obtained, these passwords can be used immediately to siphon off funds or sensitive information. For instance, a well-documented case involved employees at a large corporation falling victim to sophisticated phishing attempts, resulting in significant data breaches as their login credentials were compromised.
Additionally, brute-force attacks remain a favored technique among cybercriminals. Essentially, this approach involves systematically attempting all possible password combinations until the correct one is found. With 19 billion compromised passwords readily available, attackers can significantly shorten the process by using a list of common or previously breached passwords, thus increasing their chances of success. The dark web plays a crucial role in facilitating these malicious activities, acting as a marketplace where stolen credentials are bought and sold. Cybercriminals can easily acquire lists of compromised passwords, which fuels their operations and exacerbates the security challenges faced by users worldwide.
In conclusion, the exploitation of compromised passwords has become a fundamental tactic in the arsenal of cybercriminals. The combination of credential stuffing, phishing, brute-force attacks, and the dark web’s involvement not only underscores the importance of password security but also highlights the ongoing threats posed in the digital landscape.

Strengthening Your Security: What You Can Do to Protect Yourself
In the face of the alarming statistic of 19 billion compromised passwords, it is crucial for both individuals and businesses to implement robust security measures to protect their sensitive information. One of the most effective ways to enhance security is by using strong and unique passwords for each account. A strong password should comprise a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters, while ensuring that it does not include easily guessable information such as common words or personal details.
Additionally, enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) is a critical step that adds an extra layer of security. By requiring a second form of verification, typically through a mobile device or authenticator app, 2FA significantly decreases the likelihood of unauthorized access, even if a password has been compromised. This measure is highly recommended, especially for accounts containing sensitive data such as online banking or personal email.
Effective password management is equally important in reducing the risks associated with compromised passwords. Using a password manager can streamline this process by securely storing and generating strong passwords, minimizing the need to rely on memory and reducing the temptation to reuse passwords across multiple platforms. Furthermore, individuals and businesses should regularly monitor their accounts for suspicious activities. Early detection of unauthorized attempts to access accounts can help mitigate potential damage and prevent further breaches.
Finally, it is essential to stay informed about potential threats and security updates. Regularly reviewing security best practices and being proactive in adapting to new risks can significantly enhance overall security in an era dominated by the existence of 19 billion compromised passwords. By taking these steps, individuals and organizations can safeguard their digital assets, ensuring greater protection against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
The Future of Online Security in the Age of Massive Data Breaches
As we navigate an increasingly interconnected world, the implications of the staggering 19 billion compromised passwords loom large over the future of online security. With cyber threats evolving at an unprecedented pace, organizations and individuals must adopt progressive measures to safeguard their information. The integration of cutting-edge technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, is becoming essential in enhancing threat detection capabilities. These technologies can analyze patterns in real time, allowing for more rapid identification of unusual activities and potential breaches.
Moreover, advancements in biometric authentication present promising alternatives to traditional password protection methods. By utilizing unique physiological characteristics, such as fingerprints or facial recognition, biometric systems can enhance security by making unauthorized access significantly more difficult. As these technologies mature and gain wider acceptance, they hold the potential to drastically reduce reliance on passwords, thus mitigating the risks associated with the current landscape of compromised accounts.
In addition to technological innovations, the role of legislation and industry standards is crucial in establishing a secure digital environment. Governments are increasingly recognizing the need for stringent data protection regulations that compel organizations to implement robust cybersecurity measures. Compliance with these laws can enhance consumer confidence, foster a culture of accountability, and ultimately lead to improved data security practices across various sectors.
Furthermore, nurturing a culture of security awareness within organizations is imperative. Employees must be educated on the importance of safeguarding sensitive information and trained to recognize potential threats, such as phishing attacks. This proactive approach reduces vulnerability and enhances overall resilience against the cyber landscape’s ever-present risks.
In conclusion, the future of online security will need to be a multifaceted approach that combines innovative technologies, regulatory frameworks, and a strong emphasis on awareness to combat the implications of having 19 billion compromised passwords. By staying vigilant and embracing these changes, both individuals and organizations can work towards a safer online experience.